AI-Powered Vulnerability Triage with GitHub Security Lab Taskflow Agent | AI vulnerability triage
Key Takeaways
- The GitHub Security Lab uses large language models (LLMs) to streamline vulnerability triage.
- Taskflows designed by the lab have identified approximately 30 real-world vulnerabilities.
- LLMs effectively reduce false positives in security alerts, improving overall audit accuracy.
- The taskflow generates detailed bug report formats aiding human validation of security alerts.
- Customizable taskflows based on specific permissions help enhance the triage process further.
What We Know So Far
AI vulnerability triage — The integration of artificial intelligence into security processes is gaining momentum, particularly with GitHub Security Lab’s Taskflow Agent. This innovative tool utilizes large language models (LLMs) to assist in the triage of security alerts, an essential step in managing vulnerabilities effectively.
As reported, the Taskflow Agent has successfully identified around 30 real-world vulnerabilities, showcasing its capability to efficiently process complex audit tasks and improve security overall.
Understanding the Taskflow Agent
The Taskflow Agent incorporates a series of structured steps designed to streamline the auditing process. Each task within the taskflow operates independently while contributing to a collective review of security alerts. This organized approach is pivotal in dealing with the ever-increasing volume of alerts that developers face.
Moreover, testing conducted by the GitHub Security Lab primarily involved the Claude Sonnet 3.5 model, illustrating the practical applications of AI in reducing the tedious aspects of vulnerability management.
Key Details and Context
More Details from the Release
Each task in the taskflow independently gathers information and contributes to a collective alert review process.
The GitHub Security Lab has conducted tests using their taskflows primarily with the Claude Sonnet 3.5 model.
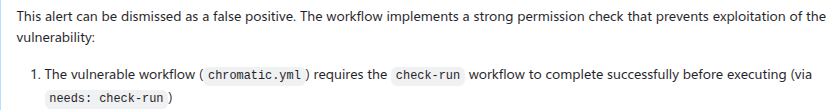
LLMs help spot false positives in security alerts, especially where access control checks are involved.
The taskflows designed for triaging involve a series of defined tasks that the LLMs execute, which helps in organizing complex auditing processes.
The triage process with the Taskflow Agent has resulted in the identification of around 30 real-world vulnerabilities.
The GitHub Security Lab is utilizing large language models (LLMs) to triage security alerts.
More Details from the Release
Taskflows can be customized based on repo-specific permission checks and analysis of dismissal reasons to reduce false positives.
The results generated by the taskflow are compiled into a bug report format that facilitates easier human validation.
Each task in the taskflow independently gathers information and contributes to a collective alert review process.
The GitHub Security Lab has conducted tests using their taskflows primarily with the Claude Sonnet 3.5 model.
LLMs help spot false positives in security alerts, especially where access control checks are involved.
The taskflows designed for triaging involve a series of defined tasks that the LLMs execute, which helps in organizing complex auditing processes.
The triage process with the Taskflow Agent has resulted in the identification of around 30 real-world vulnerabilities.
The GitHub Security Lab is utilizing large language models (LLMs) to triage security alerts.
False positives are a common obstacle in security triage, often leading to wasted time and resources. LLMs help mitigate these issues by refining the identification process. They excel in spotting potential discrepancies, particularly in scenarios involving access control checks.
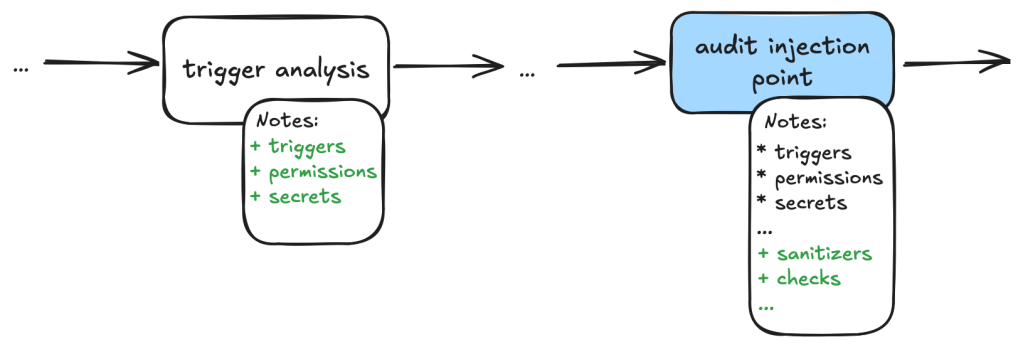
Taskflows can also be tailored to be repo-specific, allowing organizations to customize their vulnerability assessments based on specific dismissal criteria, further reducing false positives and streamlining operations.
How Taskflows are Structured
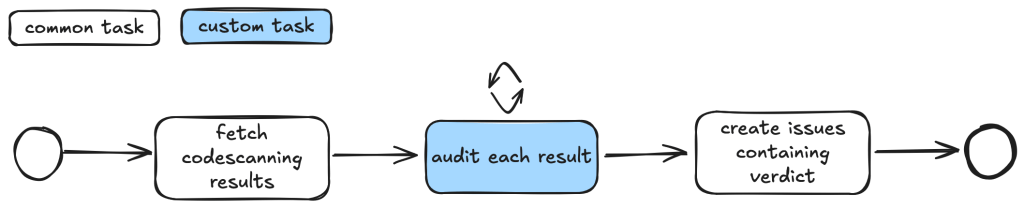
The taskflows implemented involve a defined series of actions that the LLMs execute. For instance, a typical taskflow begins by fetching code scanning results, followed by auditing each result, and ultimately creating issues that contain the verdict. This iterative structure fosters comprehensive oversight throughout the auditing process.
What Happens Next
As the GitHub Security Lab continues testing and refining the Taskflow Agent, it is crucial to monitor the progress made in identifying and addressing vulnerabilities in real time. The effectiveness of AI in security is expected to likely evolve, driven by user feedback and the ever-changing landscape of security threats.
Future enhancements may revolve around further customizing taskflows, optimizing automation, and integrating additional analytical tools, thereby potentially revolutionizing the way developers manage security alerts.
Future Directions for AI in Security
The ongoing integration of AI in security practices is an evolving field. With tools such as the Taskflow Agent, it is becoming clear that AI can provide significant assistance in making security audits more efficient. Continuous improvements in LLMs and their applications promise a future where security management is even more streamlined.
Why This Matters
The significance of AI in vulnerability management cannot be overstated. By streamlining the triage process, organizations can focus their efforts on high-priority issues, allowing resources to be allocated more effectively. As a result, the overall integrity of software products can be enhanced.
Furthermore, the collaboration between developers and AI tools like the Taskflow Agent sets the stage for a new era of proactive security measures, moving beyond traditional reactive approaches that often fall short.
Balancing AI and Human Oversight
While AI can significantly aid in vulnerability management, human oversight remains crucial. The detailed bug reports generated by the taskflow enable developers to validate alerts effectively, ensuring that AI serves as an assistant rather than a sole decision-maker.
FAQ
As the utilization of AI in vulnerability triage expands, ongoing questions is expected to emerge regarding its application, challenges, and effectiveness.
Engaging with these concerns is expected to be key to refining AI tools and processes, ensuring they meet the demands of developers and organizations alike.

